Oral leukoplakia (OL) is a clinical term for a nonremovable white lesion that is not easily recognisable as any particular condition and therefore requires further investigation.
Oral leukoplakia manifests as patches that are bright white and sharply defined. The surfaces of the patches are slightly raised above the surrounding mucosa.
Oral leukoplakia may be homogenous (uniform lesion often with a fissured surface), or nonhomogeneous (with surface irregularity and textural or colour variation for example speckled-see below given photograph.
 |
| Leukoplakia of the ventral surface of the tongue and floor of mouth |
Some oral leukoplakia lesions show histologic evidence of dysplasia, carcinoma in situ or invasive squamous cell carcinoma.
The malignant transformation rate for oral leukoplakia is variably reported, but ranges between 0.13 to 34%, with a mean annual transformation rate of 3.8% per year.
Refer patients with oral leukoplakia to an appropriate specialist for biopsy and monitoring.
Biopsy of a persistent undiagnosed oral white patch is required to exclude epithelial dysplasia, carcinoma in situ and squamous cell carcinoma.
Oral Hairy Leukoplakia
It is most commonly found on the lateral margin of the tongue; usually bilateral.
The term hairy Leukoplakia indicates the corrugated surface of the epithelium.
It is associated with EBV infection (lateral aspect of tongue may harbour the EBV in latent stage.
Oral candidiasis and OHL are predictive indicators for subsequent development of AIDS in HIV seropositive patients.
Clinical Features
It is a painless, faint white vertical streaks or thickened and furrowed areas with a shaggy keratotic surface.
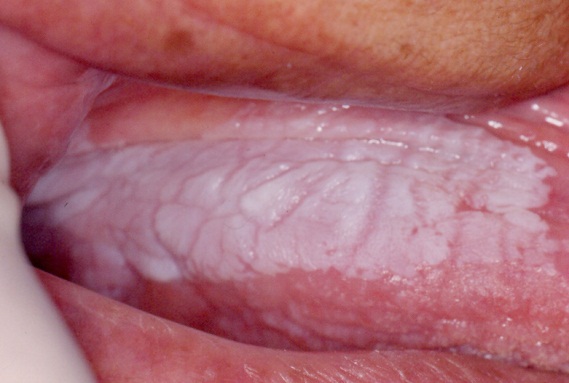 |
| Hairy Leukoplakia of the tongue [3] |
Ref:
1. Therapeutic guidelines 2019
2. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41379-019-0444-0#Sec6
2. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41379-019-0444-0#Sec6
